Concepts
History 🔗
Kubernetes also called k8s (a “k” followed by 8 chars and a “s”) or simply kube means “Helmsman” in Greek. It is a container orchestrator inspired by Google Borg System which were orchestrating billions of containers on Google infrastructure.
Version v1.0.0 of Kubernetes was released in July 2015, the last version as of today (October 2024) is v1.31.1. The release cycle is quite fast with 3 minor releases per year.
Main functionalities 🔗
Kubernetes is a container orchestrator offering main functionalities, such as:
- Management of applications running in containers
- Self-healing
- Service discovery
- Usage of Secrets and Configurations
- Long-running process and batch jobs
- Role Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Storage Orchestration
Manages applications in production 🔗
environments
Major project in the open-source ecosystem 🔗
Kubernetes is the first graduated project within the CNCF, it was followed by major players like etcd and Prometheus

CNCF
What is a Kubernetes cluster made of ? 🔗
A Kubernetes cluster is composed of nodes, where a node is either a virtual machine or a bare metal server. A node can belong to the Control Plane which run processes in charge of managing the cluster and the applications running on it. Or, a node can be a Worker dedicated to run Pods, a group of containers sharing a network stack and storage.
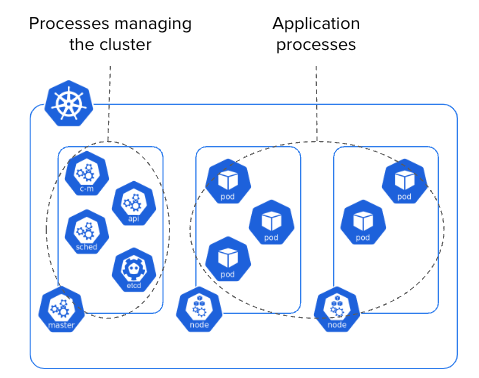
cluster
How to access a cluster 🔗
A cluster usually comes with a kubeconfig file which contains all the information to communicate with the cluster API Server. This file can be used to configure the standard kubectl binary to manage the cluster. The kubeconfig file can also be used with tools like k9s, Mirantis Lens, … which give a higher level view of the cluster.
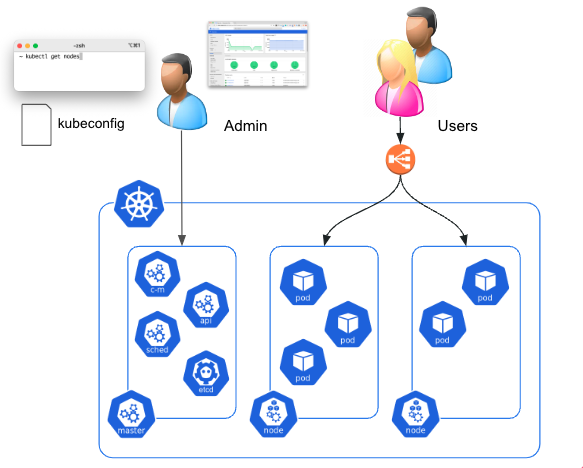
access
Various workload resources for different use cases 🔗
To run a Pod we often rely on a higher level resource, instead of running it directly. The workload resources are:
- Deployment : web server
- DaemonSet : one agent per node
- Job / CronJob : batch
- StatefulSet : stateful application
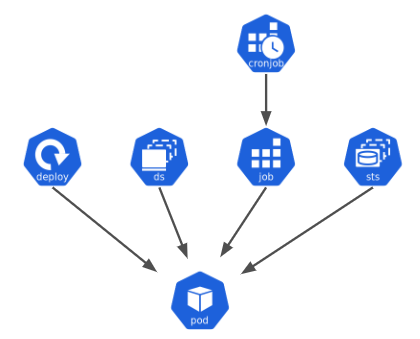
workload resources
A request that reaches a Service is load-balanced between the exposed Pods
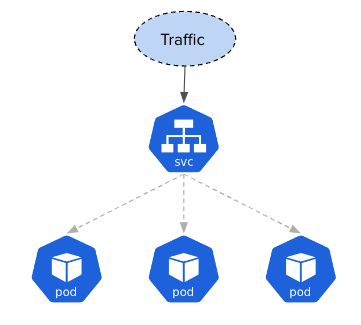
service
A Pod can use several resources
- ConfigMap : contains configuration data
- Secret : contains sensitive data
- PersistentVolumeClaim / PersistentVolume : storage management
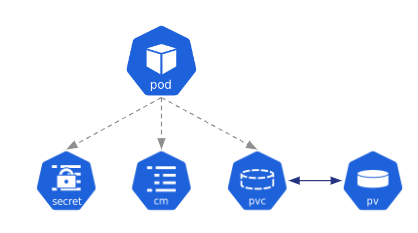
pod resources
Several types of resources 🔗
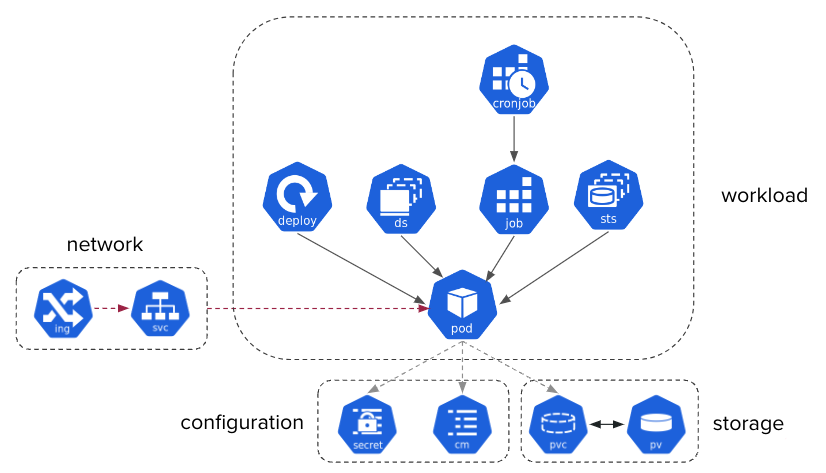
Summary
An application runs in a Namespace 🔗
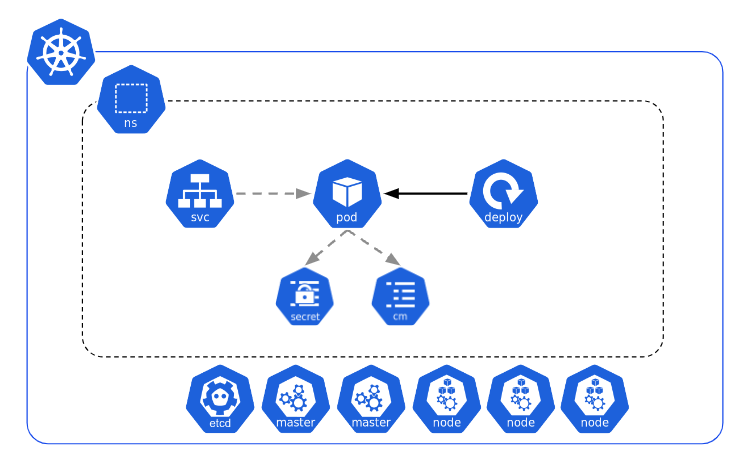
Namespace
Resource creation 🔗
Each resource is defined in a YAML specification which is sent to the API Server using the kubectl binary.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: www
spec:
containers:
- name: www
image: nginx:1.24
kubectl apply -f www.yaml